힉스 보손(Higgs boson)와 힉스 필드(Higgs field)
가장 진보된 과학 개념 중 하나는 힉스 보손으로, "신의 입자"라고도 불립니다. 힉스 보손은 2012년에 스위스 제네바 인근 CERN의 대형하드론충돌기(LHC)에서 발견된 기본 입자입니다. 이것은 우주 곳곳에 존재한다고 여겨지는 에너지의 영역인 힉스 필드와 관련되어 있습니다.
힉스 필드는 입자가 질량을 얻는 방식을 이해하는 데 중요합니다. 이론에 따르면, 입자는 힉스 필드와 상호작용하여 질량을 얻습니다. 입자가 필드와 더 많이 상호작용할수록 더 많은 질량을 가집니다. 힉스 보손은 이 필드와 관련된 입자로, 힉스 필드의 존재와 입자가 질량을 얻는 메커니즘을 확인했습니다.
힉스 보손의 발견은 입자 물리학 분야에서 중요한 이정표였으며, 우주를 구성하는 기본 입자와 힘을 설명하는 이론적 틀인 표준 모델을 검증하는 데 도움이 되었습니다. 힉스 보손과 힉스 필드를 이해함으로써 우주의 기본 구조에 대한 우리의 지식이 깊어졌고, 알려지지 않은 다른 입자와 힘을 탐색하고 발견할 수 있는 새로운 가능성을 열어주었습니다.
힉스 보손의 발견은 입자 물리학에서 추가 질문과 연구를 이끌어냈습니다. 예를 들어, 힉스 필드는 어두운 물질의 성질에 대한 통찰력을 제공할 수 있습니다. 어두운 물질은 우주의 총 질량-에너지 함량의 약 27%를 차지하는 신비한 물질 형태로, 빛을 발산하거나 흡수하지 않아 감지하기 매우 어렵습니다. 그러나 은하와 은하단의 중력 영향은 그 존재에 대한 증거를 제공합니다.
어두운 물질은 힉스 필드와 약하게 상호작용하는 입자로 구성되어 있을 수 있으며, 이로 인해 질량을 가지지만 빛과 상호작용하지 못합니다. 힉스 필드의 특성과 힉스 보손을 이해하는 것은 결국 우리가 어두운 물질과 그것이 우주의 구조와 진화에서 차지하는 역할에 대해 더 많이 알게 될 수 있도록 도와줄 수 있습니다.
또한, 힉스 보손의 발견은 표준 모델을 넘어서 새로운 입자와 힘을 찾는 데 관심을 불러일으켰습니다. 이에는 각 알려진 입자가 아직 발견되지 않은 무거운 "슈퍼파트너" 입자를 가진다고 주장하는 초대칭성 이론이 포함됩니다. 만약 이가 사실이라면, 초대칭성은 입자 물리학에 대한 현재의 이해에 있는 일부 모순을 해결하고 우주의 기본 구성 요소에 대한 보다 포괄적인 이해를 제공할 수 있습니다.
요약하면, 힉스 보손의 발견은 가장 진보된 과학적 지식 중 하나로, 입자들이 질량을 얻는 메커니즘과 힉스 필드의 존재를 확인하는 것 뿐만 아니라 입자 물리학의 새로운 연구 방향을 열어주었습니다. 힉스 보손, 힉스 필드 및 그들의 함의에 대한 지속적인 연구는 의심의 여지없이 흥미로운 발견과 우주의 근본적인 구조에 대한 더 깊은 이해를 이끌 것입니다.
힉스 보손의 발견은 또한 우주론 분야에서의 연구를 촉진시켰으며, 특히 초기 우주의 조건과 우주 팽창 과정을 이해하는 데 중요합니다. 우주 팽창은 빅뱅 직후에 우주가 극도로 빠르게 확장된 것으로 제안하는 널리 받아들여지는 이론입니다. 이 급속한 확장은 힉스 필드와 유사한 스칼라 필드에 의해 주도되었다고 생각됩니다.
힉스 필드와 힉스 보손을 연구함으로써 우주 팽창을 주도한 스칼라 필드의 성질에 대한 귀중한 통찰력을 얻을 수 있으며, 초기 우주의 역학과 은하 및 은하단과 같은 대규모 구조의 형성에 대한 이해를 개선할 수 있습니다.
게다가, 힉스 보손과 관련된 힉스 필드는 중력 연구와 중력에 대한 양자 이론 탐색에 영향을 미칩니다. 표준 모델은 전자기력, 약력, 강력한 힘을 설명하는 데 성공했지만, 중력은 알버트 아인슈타인의 일반 상대성 이론으로 설명되며 포함되지 않습니다. 이론물리학에서 오랜 도전 과제 중 하나는 일반 상대성 이론과 양자역학을 통합할 수 있는 일관된 중력 양자 이론을 개발하는 것입니다.
힉스 필드는 입자에 질량을 부여하는 스칼라 필드이므로, 그 특성을 이해하는 것은 연구자들이 중력에 대한 양자 이론을 개발하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 이는 우주의 기본 힘과 입자에 대한 더 완전한 이해를 제공할 뿐만 아니라, 블랙홀과 시공간의 본질과 같은 현상에 대한 우리의 이해에 깊은 함의를 가지게 될 것입니다.
결론적으로, 힉스 보손은 입자 물리학, 우주론, 이론 물리학 등 다양한 연구 분야에서 중요한 고급 과학 지식입니다. 그 발견은 새로운 연구 방향을 열어놓았으며, 인간의 이해의 경계를 밀어내고 앞으로 흥미로운 발견을 가능케 했습니다.
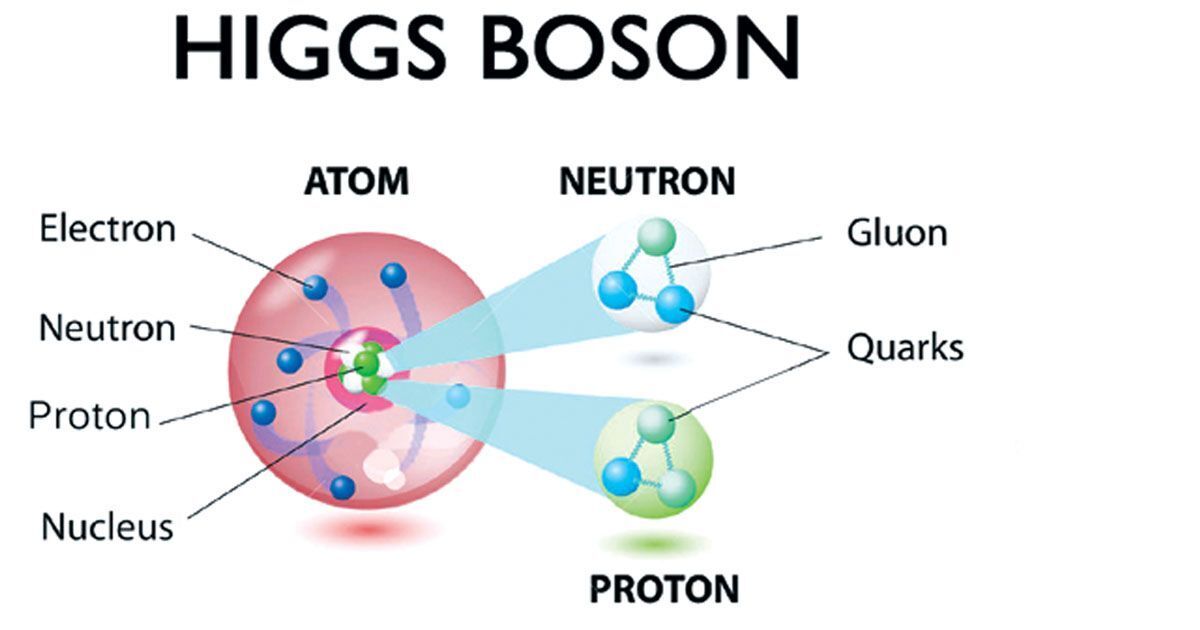
One of the most advanced scientific concepts is the Higgs boson, also known as the "God particle." The Higgs boson is a fundamental particle discovered in 2012 at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in CERN, near Geneva, Switzerland. It is associated with the Higgs field, a field of energy that is believed to exist throughout the universe.
The Higgs field is crucial in understanding how particles acquire mass. According to the theory, particles gain mass by interacting with the Higgs field. The more they interact with the field, the more mass they have. The Higgs boson is the particle associated with this field, and its discovery confirmed the existence of the Higgs field and the mechanism through which particles acquire mass.
The discovery of the Higgs boson was a significant milestone in the field of particle physics and helped to validate the Standard Model, which is the theoretical framework describing the fundamental particles and forces that make up our universe. Understanding the Higgs boson and the Higgs field has deepened our knowledge of the universe's fundamental structure and has opened up new possibilities for exploring and potentially uncovering other unknown particles and forces.
The Higgs boson's discovery has also led to further questions and research in particle physics. For example, the Higgs field could potentially provide insight into the nature of dark matter, an elusive and mysterious form of matter that makes up about 27% of the universe's total mass-energy content. Dark matter neither emits nor absorbs light, making it extremely difficult to detect. However, its gravitational influence on galaxies and galaxy clusters provides evidence for its existence.
One possibility is that dark matter is composed of particles that interact weakly with the Higgs field, giving them mass but not allowing them to interact with light. Understanding the Higgs field's properties and the Higgs boson could eventually help us learn more about dark matter and its role in the universe's structure and evolution.
Additionally, the discovery of the Higgs boson has sparked interest in the search for new particles and forces beyond the Standard Model. This includes theories such as supersymmetry, which posits that each known particle has a heavier "superpartner" particle yet to be discovered. If proven true, supersymmetry could help resolve some inconsistencies in the current understanding of particle physics and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the universe's fundamental components.
In summary, the discovery of the Higgs boson is among the most advanced scientific knowledge, as it has not only confirmed the existence of the Higgs field and the mechanism through which particles acquire mass, but also opened up new research directions in particle physics. The ongoing study of the Higgs boson, the Higgs field, and their implications will undoubtedly lead to exciting discoveries and a deeper understanding of our universe's underlying structure.
The Higgs boson's discovery has also fueled research in the field of cosmology, particularly in understanding the early universe's conditions and the process of cosmic inflation. Cosmic inflation is a widely accepted theory that suggests that the universe underwent an extremely rapid expansion shortly after the Big Bang. This rapid expansion is thought to have been driven by a scalar field, which is similar in nature to the Higgs field.
Studying the Higgs field and Higgs boson could provide valuable insights into the nature of the scalar field that drove cosmic inflation, potentially shedding light on the early universe's dynamics and the formation of large-scale structures like galaxies and galaxy clusters.
Furthermore, the Higgs boson and its associated Higgs field have implications for the study of gravity and the search for a quantum theory of gravity. While the Standard Model has been successful in describing the electromagnetic, weak, and strong forces, it does not include a description of gravity, which is explained by Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. One of the long-standing challenges in theoretical physics is to develop a consistent quantum theory of gravity, which could unify general relativity with quantum mechanics.
As the Higgs field is a scalar field that gives particles mass, understanding its properties could help researchers develop a quantum theory of gravity. This would not only provide a more complete understanding of the fundamental forces and particles in the universe but also have profound implications for our understanding of phenomena such as black holes and the nature of spacetime itself.
In conclusion, the Higgs boson is a crucial piece of advanced scientific knowledge, with far-reaching implications for various fields of study, including particle physics, cosmology, and theoretical physics. Its discovery has opened up new avenues of research, pushing the boundaries of human understanding and paving the way for exciting discoveries in the future.